PowerPoint VBA Macro Examples & Tutorial
Written by
Reviewed by
In this Article
- VBA PDF (Free Downloads)
- PowerPoint VBA (Macros) Tutorial
- Save As Macro-Enabled Presentation
- Enable ‘Developer’ Tab in the Ribbon
- Create PowerPoint Macro
- PowerPoint Application
- Open a New Presentation
- Open an Existing Presentation
- Open and Assign to a Variable
- Refer to Active Presentation
- Save Current Presentation
- Close Current Presentation
- Useful References
- Assign Existing Presentation (by name) to Variable
- Assign Active Slide to Variable
- Assign slide by Index to Variable
- Count Number of Slides
- Get Slide Index Number of Current Slide
- Add a Blank Slide to End of Slide Show
- Add a slide after current slide
- Delete a Slide
- Go to a Specific Slide
- Move Slide
- Loop Through All Slides
- Loop through All Shapes of Active Slide
- Loop through All shapes in All Slides
- Loop through All TextBoxes of Active Slide
- Loop through All TextBoxes in All Slides
- Copy Selected slides to new PPT Presentation
- Copy Active Slide to End of Active Presentation
- Useful PowerPoint Macro Examples
- Change Slide During Slide Show
- Change Font on All Slides in All TextBoxes
- Change Case From Upper to Normal in All TextBoxes
- Toggle Case between Upper and Normal in All TextBoxes
- Remove Underline from Descenders
- Remove Animations From All Slides
- Save Presentation As PDF
- Find and Replace Text
- Export Slide As Image
- Resize Image To Cover Full Slide
- Exit All Running Slide Shows
- Automating PowerPoint from Excel
This is a complete guide to automating PowerPoint using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) Macros. Below you will find many useful examples.
VBA PDF (Free Downloads)
Download our free Microsoft PowerPoint VBA Tutorial! Or VBA Tutorials for other Office Programs!

PowerPoint VBA (Macros) Tutorial
Save As Macro-Enabled Presentation
The Presentation with VBA code should be ‘Saved As’ PowerPoint Macro-Enabled Presentation (*.pptm)
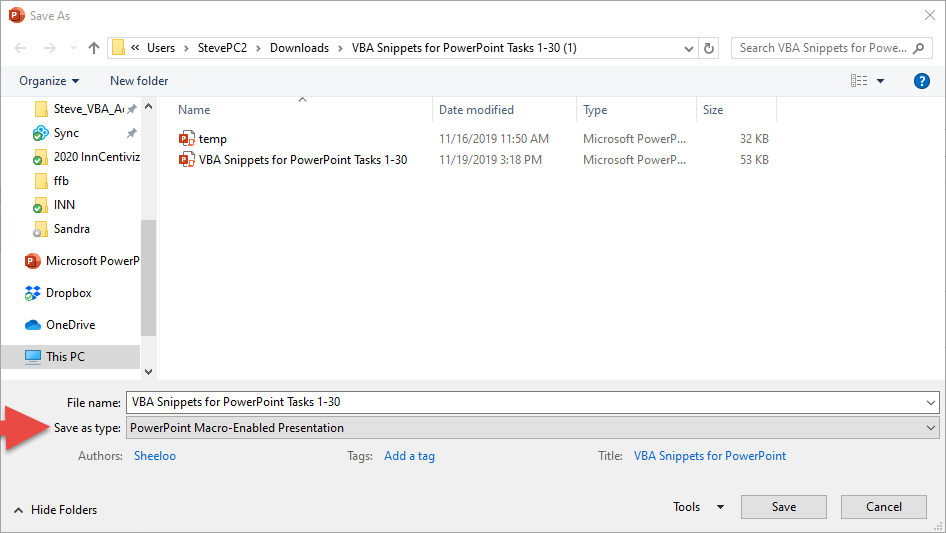
Enable ‘Developer’ Tab in the Ribbon
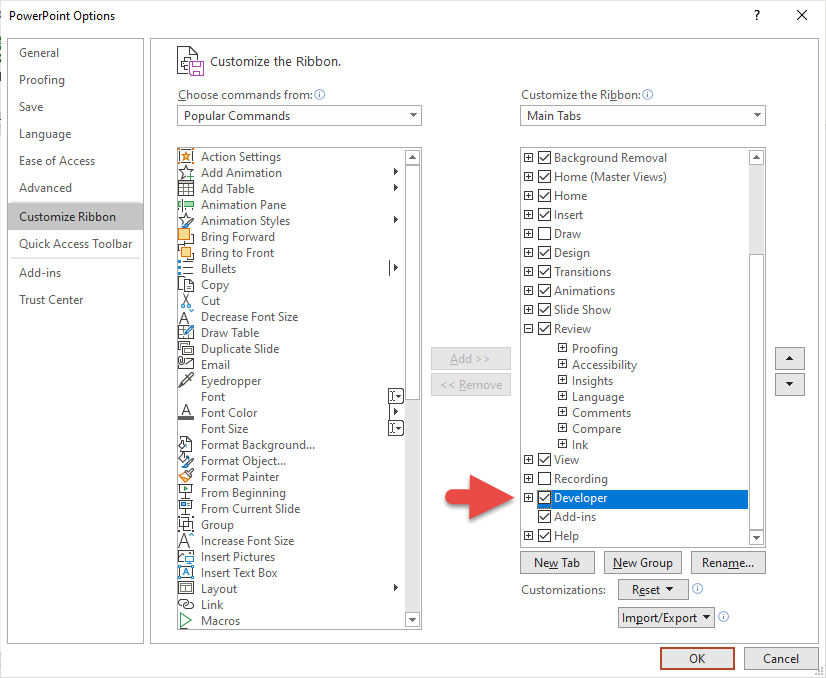
You should to enable the Developer tab on the Ribbon before creating VBA code. To do so choose File -> Options then click on ‘Customize Ribbon’ and check the box next to ‘Developer’ tab in the right pane.
Create PowerPoint Macro
This is a simple example of a PowerPoint VBA Macro:
Sub SavePresentationAsPDF()
Dim pptName As String
Dim PDFName As String
' Save PowerPoint as PDF
pptName = ActivePresentation.FullName
' Replace PowerPoint file extension in the name to PDF
PDFName = Left(pptName, InStr(pptName, ".")) & "pdf"
ActivePresentation.ExportAsFixedFormat PDFName, 2 ' ppFixedFormatTypePDF = 2
End SubIt saves the active presentation as a PDF. Each line of code does the following:
- Creates variables for the PowerPoint name and PDF name
- Assigns the active presentation name to pptName variable
- Creates the full PDF name
- Saves the presentation as a PDF
PowerPoint Application
When VBA code is running within a PowerPoint Presentation, PowerPoint Application is the default application and it can be manipulated without explicitly reference. Create a New Presentation
To create a presentation, use the Add method of PowerPoint application.
Application.Presentations.Add
' or without explicit reference
Presentations.Add
Open a New Presentation
To open a new and blank presentation use the Add method of Application.Presentations collection
Presentations.AddOpen an Existing Presentation
To open a presentation which you have already created, use the Open method of Application.Presentations collection
Presentations.Open ("My Presentation.pptx")The code above assumes that the presentation is in the same directory as the PowerPoint Presentation containing the code.
Open and Assign to a Variable
You should assign the presentation you open to a variable so that you can manipulate it as per your requirements.
Dim ppt As Presentation
Set ppt = Presentations.Open("My Presentation.pptx")Refer to Active Presentation
Use the reference ActivePresentation to manipulate the Presentation active in the GUI when the VBA code is executed.
' Print the name of the ActivePresentation to the Immediate Window
Debug.Print ActivePresentation.NameSave Current Presentation
The statement below will save the Active Presentation if it was saved before. It it has not been saved then you will be prompted with the ‘Save As’ dialog.
ActivePresentation.SaveClose Current Presentation
The statement below will close the Active Presentation even if it was not saved after the last edit.
ActivePresentation.CloseUseful References
Assign Existing Presentation (by name) to Variable
Dim myPresentationByName As Presentation
Set myPresentationByName = Application.Presentations("My Presentation")Assign Active Slide to Variable
Dim currentSlide As Slide
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.SlideAssign slide by Index to Variable
Dim mySlide As Slide
Set mySlide = ActivePresentation.Slides(11)Count Number of Slides
Dim slideCount As Long
slideCount = ActivePresentation.Slides.CountGet Slide Index Number of Current Slide
Dim currentSlideIndex As Integer
currentSlideIndex = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.SlideIndexAdd a Blank Slide to End of Slide Show
Dim slideCount As Long
Dim newSlide as Slide
slideCount = ActivePresentation.Slides.Count
Set newSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides.Add(slideCount + 1, 12)
' or as ppLayoutBlank = 12
Set newSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides.Add(slideCount + 1, ppLayoutBlank)Add a slide after current slide
Dim newSlide As Slide
Dim currentSlideIndex as Integer
currentSlideIndex = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.SlideIndex
Set newSlide = ActivePresentation.Slides.Add(currentSlideIndex, ppLayoutBlank)Delete a Slide
Dim currentSlideIndex as Integer
currentSlideIndex = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.SlideIndex
ActivePresentation.Slides(currentSlideIndex).DeleteGo to a Specific Slide
' This will take you to slide number 4
Application.ActiveWindow.View.GotoSlide (4)Move Slide
You can move a slide from its old position to the new position
' Move from slide 3 to first slide
Dim oldPosition as integer, dim newPosition as integer
oldPosition = 3
newPosition = 1
ActivePresentation.Slides(oldPosition).MoveTo toPos:=newPositionLoop Through All Slides
You can do something with each slide or go through all slides to find a few slides and do something about with using the code;
Dim mySlide as Slide
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
' Do something with the current slide referred to in variable 'mySlide'
' Debug.Print mySlide.Name
Next SlideLoop through All Shapes of Active Slide
The power of PowerPoint can be realized by using ‘Shapes.’ The code below loops through all the shapes on the current slide so that you can manipulate them as you want;
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim shp as Shape
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Do something with the current shape referred to in variable 'shp'
' For example print the name of the shape in the Immediate Window
Debug.Print shp.Name
Next shpLoop through All shapes in All Slides
You can loop through all the shapes in the presentation by adding a loop to go through all slides.
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim shp as Shape
For Each currentSlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Do something with the current shape referred to in variable 'shp'
Debug.Print shp.Name
Next shp
Next currentSlideLoop through All TextBoxes of Active Slide
TextBoxes are the most often used Shape in PowerPoint presentations. You can loop through all the Text Boxes by adding a check for ‘Shape Type.’ TexBoxes have the shape type defined as the VBA constant msoTextBox (the numerical value of the constant is 17)
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim shp as Shape
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Check if the shape type is msoTextBox
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
'Print the text in the TextBox
Debug.Print shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Text
End If
Next shpLoop through All TextBoxes in All Slides
Again, you can loop through all the textboxes in the presentation by adding a loop to go through all slides.
Dim currentSlide as Slide Dim shp as Shape
For Each currentSlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In currentSlide.Shapes
' Check if the shape type is msoTextBox
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Do something with the TextBox referred to in variable 'shp'
Debug.Print shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Text
End If
Next shp
Next currentSlideCopy Selected slides to new PPT Presentation
To copy certain slides to a new presentations, first select the desired slides in the existing presentation and then run the code below;
Dim currentPresentation as Presentation
Dim currentSlide as Slide
Dim newPresentation as Presentation
' Save reference to current presentation
Set currentPresentation = Application.ActivePresentation
' Save reference to current slide
Set currentSlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide
' Add new Presentation and save to a reference
Set NewPresentation = Application.Presentations.Add
' Copy selected slides
Selection.Copy
' Paste it in new Presentation
NewPresentation.Slides.PasteCopy Active Slide to End of Active Presentation
' Copy current slide
Application.ActiveWindow.View.Slide.Copy
' Paste at the end
ActivePresentation.Slides.PasteUseful PowerPoint Macro Examples
Here are some useful macro examples showing how to do tasks. These will also demonstrate the concepts described above.
Change Slide During Slide Show
Sub ChangeSlideDuringSlideShow()
Dim SlideIndex As Integer
Dim SlideIndexPrevious As Integer
' Change Current slide to selected slide 4 during during slide show
SlideIndex = 4
' Index of the current slide show window is 1 in the SlideShowWindows collection
SlideIndexPrevious = SlideShowWindows(1).View.CurrentShowPosition
SlideShowWindows(1).View.GotoSlide SlideIndex
End SubChange Font on All Slides in All TextBoxes
Sub ChangeFontOnAllSlides()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Change Font Size on all Slides
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Change Fontsize to 24
shp.TextFrame.TextRange.Font.Size = 24
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubChange Case From Upper to Normal in All TextBoxes
Sub ChangeCaseFromUppertoNormal()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Change From Upper Case to Normal Case for all slides
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Change Upper Case to Normal Case
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Allcaps = False
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubToggle Case between Upper and Normal in All TextBoxes
Sub ToggleCaseBetweenUpperAndNormal()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Toggle between Upper Case and Normal Case for all slides
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Toggle between Upper Case and Normal Case
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Allcaps = _
Not shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Allcaps
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubRemove Underline from Descenders
In typography, a descender is the portion of a letter that extends below the baseline of a font. In most fonts, descenders are reserved for lowercase characters such as g, j, q, p, y, and sometimes f.
When you underline text, it does not look nice under descenders. Here is the code to remove underline from all such characters g, j, p, q, and y in the whole Presentation.
Sub RemoveUnderlineFromDescenders()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
Dim descenders_list As String
Dim phrase As String
Dim x As Long
' Remove underlines from Descenders
descenders_list = "gjpqy"
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
' Remove underline from letters "gjpqy"
With shp.TextFrame.TextRange
phrase = .Text
For x = 1 To Len(.Text)
If InStr(descenders_list, Mid$(phrase, x, 1)) > 0 Then
.Characters(x, 1).Font.Underline = False
End If
Next x
End With
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubRemove Animations From All Slides
Use the code below to remove all animations set in a Presentation.
Sub RemoveAnimationsFromAllSlides()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim i As Long
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For i = mySlide.TimeLine.MainSequence.Count To 1 Step -1
'Remove Each Animation
mySlide.TimeLine.MainSequence.Item(i).Delete
Next i
Next mySlide
End SubSave Presentation As PDF
You can easily save Active Presentation in PDF format.
Sub SavePresentationAsPDF()
Dim pptName As String
Dim PDFName As String
' Save PowerPoint as PDF
pptName = ActivePresentation.FullName
' Replace PowerPoint file extension in the name to PDF
PDFName = Left(pptName, InStr(pptName, ".")) & "pdf"
ActivePresentation.ExportAsFixedFormat PDFName, 2 ' ppFixedFormatTypePDF = 2
End SubFind and Replace Text
You can find and replace text in All TextBoxes of All Slides. After the fist instance of the text you want to find (defined by findWhat) you need to loop through the Find command to find other instances, if any.
Sub FindAndReplaceText()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
Dim findWhat As String
Dim replaceWith As String
Dim ShpTxt As TextRange
Dim TmpTxt As TextRange
findWhat = "jackal"
replaceWith = "fox"
' Find and Find and Replace
For Each mySlide In ActivePresentation.Slides
For Each shp In mySlide.Shapes
If shp.Type = 17 Then ' msoTextBox = 17
Set ShpTxt = shp.TextFrame.TextRange
'Find First Instance of "Find" word (if exists)
Set TmpTxt = ShpTxt.Replace(findWhat, _
Replacewhat:=replaceWith, _
WholeWords:=True)
'Find Any Additional instances of "Find" word (if exists)
Do While Not TmpTxt Is Nothing
Set ShpTxt = ShpTxt.Characters(TmpTxt.Start + TmpTxt.Length, ShpTxt.Length)
Set TmpTxt = ShpTxt.Replace(findWhat, _
Replacewhat:=replaceWith, _
WholeWords:=True)
Loop
End If
Next shp
Next mySlide
End SubExport Slide As Image
You can export Current SLide (or any other slide) as a PNG or JPG (JPEG) or BMP image.
Sub ExportSlideAsImage()
Dim imageType As String
Dim pptName As String
Dim imageName As String
Dim mySlide As slide
' Export current Slide to Image
imageType = "png" ' or jpg or bmp
pptName = ActivePresentation.FullName
imageName = Left(pptName, InStr(pptName, ".")) & imageType
Set mySlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.slide
mySlide.Export imageName, imageType
End SubResize Image To Cover Full Slide
Sub ResizeImageToCoverFullSlide()
Dim mySlide As slide
Dim shp As Shape
' Resize Image to full slide size
' Change height and width of the first shape on the current slide
' to fit the slide dimensions
Set mySlide = Application.ActiveWindow.View.slide
Set shp = mySlide.Shapes(1)
''
'' Replace two statemetns above with
'' the following statement if you want to
'' expand the currently selected shape
'' will give error if nothing is selected
'Set shp = ActiveWindow.Selection.ShapeRange(1)
With shp
.LockAspectRatio = False
.Height = ActivePresentation.PageSetup.SlideHeight
.Width = ActivePresentation.PageSetup.SlideWidth
.Left = 0
.Top = 0
End With
End SubExit All Running Slide Shows
If you have multiple Slide Shows open at the same time then you can close all of them using the macro below.
Sub ExitAllRunningSlideShows()
Do While SlideShowWindows.Count > 0
SlideShowWindows(1).View.Exit
Loop
End SubAutomating PowerPoint from Excel
You can also connect to PowerPoint though other applications (like Excel and Word). As as first step, you must refer to an instance of PowerPoint.
There are two ways of doing it – early binding and late binding .
Open PowerPoint – Early Binding
In ‘Early Binding’ you must explicitly set a reference to ‘Microsoft PowerPoint 16 Object Library’ (for MS Office 2019) in the VBE (Visual Basic Editor) using the option Tools->References.
' Early Binding
Dim pptApp As Application
Set pptApp = New PowerPoint.ApplicationOpen PowerPoint – Late Binding
In ‘Late Binding’ application variable is declared as an object and VBA engine connects to the correct application at run time.
' Late Binding
Dim pptApp As Object
Set pptApp = CreateObject("PowerPoint.Application")Make Application Visible
After setting the reference to PowperPoint application, you may need to make it visible.
pptApp.Visible = TrueManiplulate PowerPoint
You can use all the methods to manipulate presentations, from within PowerPoint, described above from Excel by just adding the reference to PowerPoint created by you above.
For example
Presentations.Open ("My Presentation.pptx")has to be used liked this
pptApp .Presentations.Open ("My Presentation.pptx")Close the Application
Once you have completed what you wanted to do with the PowerPoint application you must close it and should release the reference.
pptApp.Quit
Set pptApp = NothingCopy From Excel to PowerPoint
This code will copy a range from Excel to PowerPoint:
Note: It has been kept as simple as possible to show how a range from Excel can be copied to PowerPoint using VBA.
Sub copyRangeToPresentation()
' Open New PowerPoint Instance
Set pptApp = CreateObject("PowerPoint.Application")
With pptApp
' Create A New Presentation
Set ppt = .Presentations.Add
' Add A Blank Slide
Set newSlide = ppt.Slides.Add(1, 12) ' ppLayoutBlank = 12
' Copy Range from Active Sheet in Excel
ActiveSheet.Range("A1:E10").Copy
' Paste to Powerpoint as an Image
newSlide.Shapes.PasteSpecial DataType:=2 '2 = ppPasteEnhancedMetafile
' Switch to PowerPoint
.Activate
End With
End SubPowerPoint VBA FAQs
What are macros in PPT?
A Macro is a general term that refers to a set of programming instructions that automates tasks. PowerPoint (PPT) Macros automate tasks in PowerPoint using the VBA programming language.
How do I use VBA in PowerPoint?
To use VBA in PowerPoint, open the VBA Editor (ALT + F11 or Developer > Visual Basic).
How do I create a Macro in PowerPoint?
1. Open the VBA Editor (ALT + F11 or Developer > Visual Basic)
2. Go to Insert > Module to create a Code Module
3. Type ‘Sub HelloWorld’ and press Enter
4. In between the lines ‘Sub HelloWorld’ and ‘End Sub’, type ‘MsgBox “Hello World!’
5. You’ve created a Macro!
6. Now press ‘F5’ to run the Macro
Written by: Vinamra Chandra